What is DNS?
Domain Name System (DNS) is a protocol that allows us to use human readable names to communicate over networks, rather than having to manage and memorize IP addresses.
What is DNS?
TheDomain NameSystem (DNS) is a core network service that allows devices to communicate much like we do on our smart phones. Generally we don’t memorize phone numbers any more, we just save them under names in our Contacts app.
DNS works the same way, where we assign an IP address to a name. If a device doesn’t know the IP address or name of a device with which it needs to communicate, it will find that information from DNS servers either on the local network or on the Internet.
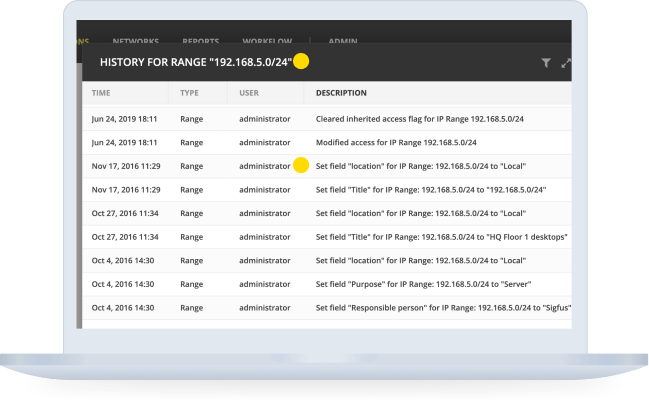
Add a DNS server Using Micetro, by Men&Mice
- Go to the web UI and click on Admin
- Click on Server Configuration
- Click Add a New DNS Server
DNS Management
DNS Management is software which allows you to view and control parts or all of your DNS architecture.
Companies will have several DNS servers to manage their Enterprise Networks in order to both load balance, but also manage internal and external DNS, as well as DNS on-premises and in the cloud for multicloud architectures. Using a Sustainable DDI solution such as Micetro, by Men&Mice can help ease the management workload by allowing network engineers to manage and view all their DNS services in one place.
Beyond management and visibility, there is the important component of implementing access control to DNS as well. Men&Mice uses Role Based Access Control to ensure the proper level of permissions are given to users and any changes are logged.
Why is DNS Necessary?
The primary identifier of a network device is the IP address. Due to the limited number of IP addresses available, IP assignments are temporary and cumbersome for users. DNS offers a higher-level, more permanent abstraction for the network and better usability for its users.
With DNS, users can use the network even if its components are changed with their IP addresses reassigned. For example, menandmice.com will always be menandmice.com even if it’s connected network device (the webserver) is moved or reconfigured.
More advanced use cases for DNS include sophisticated routing for constantly shifting networks. For example, managing the high-speed mobile internet connections of 5G or delivering content such as media or gaming faster by routing the user's request to the network edge and geographically closer to the endpoint.
What are the main components of DNS?
DNS is a hierarchical and distributed system designed to reflect administrative responsibility.
At the highest level of authority, 13 root name servers store information about the numerous Top Level Domain (TLD) name servers, which can be queried for details about the innumerable DNS name servers.
To ensure uninterrupted operation and distribute workloads, DNS servers are often configured in primary/secondary relationships. The primary server is synchronized to a number of secondary servers for redundancy. Changes are made to the primary server and propagated to the secondaries.